What is a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)?
November 13, 2022

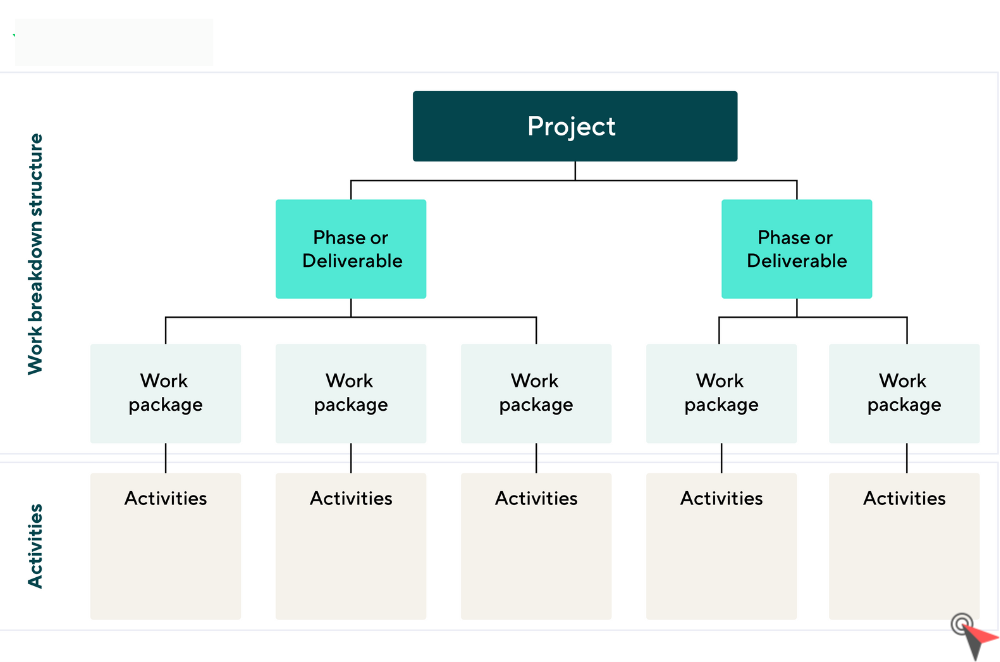
Also known as WBS, the purpose of the work breakdown structure is to make it easier to manage large, multi-stage projects. It does this by breaking projects down into smaller tasks and processes. These individual tasks can then be processed and performed simultaneously by different teams or team members, allowing for faster and more efficient execution of projects.
A work breakdown structure is in the form of a detailed diagram, identifying and breaking down the deliverables and associated activities needed to achieve it. The main and final deliverable is located at the top of the diagram, and the subtasks are organized below. The work breakdown structure is often used in conjunction with a Gantt chart and IT project management software to improve the planning and execution of otherwise colossal projects.
The work breakdown structure is generally divided into three distinct types: deliverable-based structure, phase-based structure, and responsibility-based structure.
This approach identifies the links between the scope of the project and its deliverables. It breaks down the scope into smaller, more manageable, usually more specific deliverables that must be produced, delivered, or obtained by performing project tasks to satisfy project requirements.
The phase-based work breakdown structure breaks down the project into five distinct stages: Initiate, Plan, Execute, Control, and Close. Each of these stages includes unique deliverables.
A breakdown based on responsibilities defines the structure of the project based on the teams, individuals and organizational units that will work on it. While the second level of the structure identifies who is responsible for completing the tasks, subsequent levels follow a similar format to other types of work breakdown structures, identifying the deliverables that must be completed to move the project forward. in general.
There are also several less common approaches to work breakdown structure. Let us mention in particular:
As mentioned earlier, the work breakdown structure takes the form of a diagram with the final deliverable at the top and all the sub-elements organized below. These sub-elements are generally divided into four distinct levels. This makes it easier for teams to visualize the steps needed to complete the project. The four levels of a work breakdown structure are top level, control accounts, work packages, and activities.
At the top of the diagram is the final deliverable. The top level can also be the project title.
The second level includes the different main phases of the project. These are the secondary deliverables that must be completed to ensure the success of a project.
Work packages sit below the level of control accounts and identify the tasks necessary to complete secondary deliverables.
This principle also addresses risk and uncertainty using milestones. The final level set includes the activities that facilitate the work packages.
In fact, each level is supported by the level that follows it. In a traditional breakdown diagram, this results in a branching chart that descends from the final deliverable, taking into account all the essential tasks, activities and deliverables that must be completed to complete the project.
Although the aforementioned approach may be the most widely used for work breakdown structure diagrams, it is not the only option. There are several variations of the classic WBS diagram, including:
As described above, the tree work breakdown structure represents the workflow as branching elements from the main project deliverable. Each level is made up of tasks that support the level above them. This is the most common approach to WBS diagrams.
Although not as detailed as other options, the work breakdown structure list may be the easiest option for organizations that simply need a quick overview of deliverables and subtasks. . It’s more than a checklist that lists and breaks down important tasks.
All the information presented in the tree structure can be just as easily represented and organized using a spreadsheet. The spreadsheet approach uses columns and rows to detail the different levels, tasks and deliverables. Spreadsheets are often dynamic shared documents that can be updated in real time to reflect project changes.
With project management software, companies can create detailed Gantt charts that can connect relevant information, fix mismatches, set milestones, and more. These charts are similar to spreadsheets in that they allow for dynamic updating, but they also function as a timeline templates for the project itself.
Regardless of the format of the diagram, there are five steps to creating a work breakdown structure.
Determine the scope and objectives of the project, as well as the people who will be involved. Describe the whole project and its purpose.
Determine the milestones, tasks, activities, and deliverables that will guide the project through to completion. Organize these elements into a series of phases.
Identify the specific deliverables associated with each phase. List them and identify the conditions under which each deliverable will be successfully completed.
Break down the deliverables from the previous step into constituent tasks and subtasks. List these tasks sequentially.
Once all relevant tasks have been identified and organized by phase, assign them to the teams and individuals who will be responsible for completing them. Empower teams to act on the project and provide the resources and tools they might need.
The work breakdown structure makes it easier to manage complex, multi-stage projects. But often, just trying to break these projects down can be a complex and difficult process. WBS software is a type of tool designed to streamline and automate various aspects of a work breakdown structure.
A well-designed work breakdown structure should use visualization techniques to clearly describe the various elements that make up a project and explain in detail how these elements support each other to achieve the desired goal. Knowing this, here are several best practices for creating a work breakdown structure.
The work breakdown structure should not omit any task, no matter how small. At each level, the deliverable must consist of the sum total of the work detailed in the level below.
The purpose of the work breakdown structure is to make complex projects easier to understand. It should be easy to understand for all participants without the need for detailed explanations.
Don’t waste time doing separate tasks for work already covered in another task. Make tasks mutually exclusive.
Tasks should be sufficiently broken down so that they can be completed by one person in a reasonable time.
While it’s important to consider all of the tasks that are related to a project, don’t go overboard. Creating too many subtasks can make the project confusing and overwhelming. Five levels or less should be enough to simplify the most complex projects.
Individual tasks should be trackable, made up of concrete deliverables, and backed by milestones and completion dates. This helps to measure and improve the effectiveness of the work breakdown structure.
The work breakdown structure should provide an accurate representation of the scope of the project. If the project itself changes, or if it becomes clear that the structure has flaws, managers should be prepared to revise it at some level.
IT Business Management (ITBM) from ChallengingVoice enables companies to easily plan, prioritize and track tasks associated with business objectives. Built on the Now Platform, ITBM integrates real-time updates, offers a unique data model, is fully compatible with mobile devices and supports PPM, APM and Agile solutions. In other words, ITBM is an essential resource for creating effective work breakdown structures.
Dive deeper into the work breakdown structure in ITBM, and turn your most complex projects into streamlined, easy-to-manage processes.
