Top AI Tools for Telemedicine and Virtual Healthcare in 2025
December 9, 2024
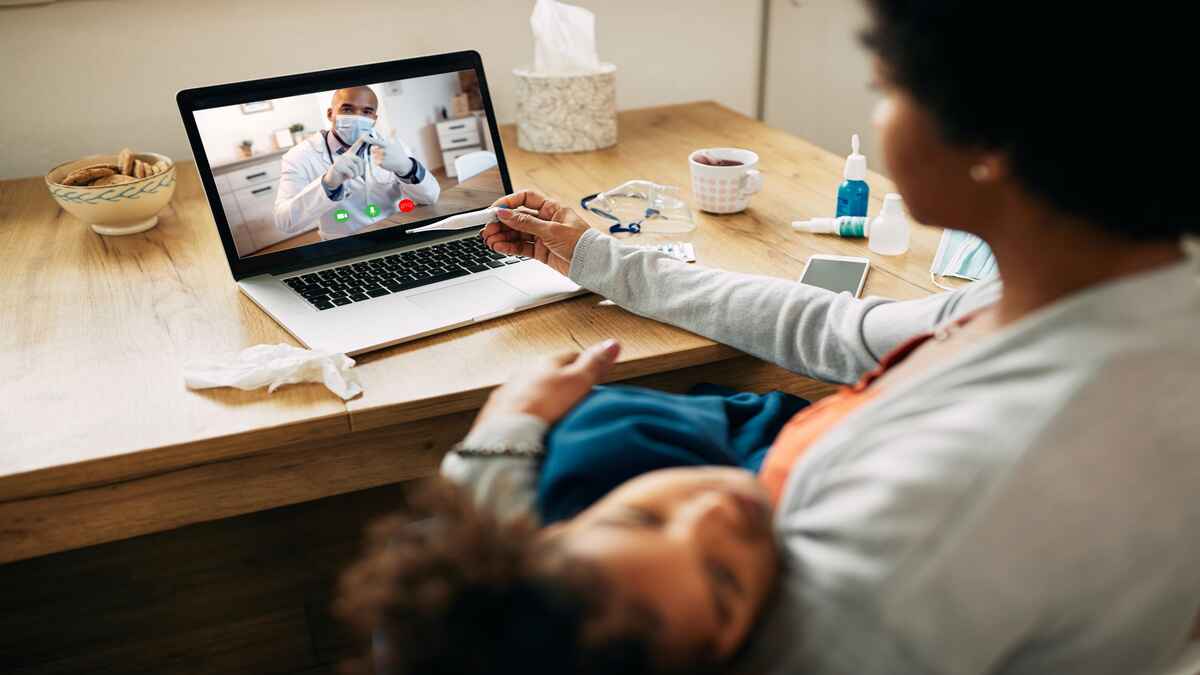


The healthcare landscape is rapidly transforming, driven by technological advancements and changing patient expectations. One of the most significant developments in recent years has been the rise of telemedicine and virtual healthcare. These innovative approaches leverage technology to deliver healthcare services remotely, offering convenience, accessibility, and improved patient outcomes. By effectively utilizing AI robotics tools with telemedicine and virtual healthcare platforms, healthcare providers can enhance patient care, improve surgical precision, and expand access to quality healthcare services, even in remote and underserved areas.
Telemedicine refers to the practice of providing healthcare services remotely using telecommunication technologies. It encompasses various services, including consultations, diagnosis, and treatment. Virtual healthcare, on the other hand, is a broader term that encompasses telemedicine as well as other digital health solutions, such as mobile health apps and wearable devices.
Artificial intelligence (AI) has emerged as a powerful tool, revolutionizing the healthcare industry. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and make accurate predictions. In the context of telemedicine and virtual healthcare, AI can be used to:
AI-powered diagnostic tools can analyze medical images and patient data to identify diseases and conditions more accurately and efficiently.
AI algorithms can develop personalized treatment plans based on patient data and preferences.
AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can provide patients with 24/7 support and education.
AI can streamline administrative tasks like scheduling appointments and managing medical records.
Telehealth eliminates the need for physical proximity, making healthcare services available to individuals in rural or underserved areas.
Virtual appointments can often be scheduled more quickly than in-person visits, reducing wait times.
Telehealth appointments can be scheduled at times convenient for patients and providers.
Patients can avoid taking time off work to attend appointments, saving time and money.
Telehealth reduces the need for travel, especially for follow-up appointments or routine check-ins.
AI-powered tools can analyze patient data to develop tailored treatment plans.
Remote monitoring devices allow continuous tracking of vital signs and other health metrics, enabling early intervention.
Patients can access educational materials and resources online, promoting self-management and health literacy.
Telehealth providers can reduce overhead costs associated with physical clinics, such as rent, utilities, and staffing.
Patients can save on transportation costs, such as gas, parking, and public transportation.
Telehealth can streamline administrative processes, increasing efficiency and cost savings.
A leading telehealth platform that connects patients with licensed physicians for virtual consultations.
24/7 availability, wide range of specialties, easy-to-use platform.
Limited availability in some areas, potential wait times.
Varies depending on the plan and coverage.
A comprehensive telehealth platform offering virtual visits with doctors, therapists, and specialists.
Wide range of services, user-friendly platform, secure communication.
Pricing can be higher than other options; not all insurance plans are accepted.
Varies depending on the plan and services.
A telehealth platform providing on-demand access to doctors and mental health professionals.
Easy to use, quick appointment scheduling, and convenient for urgent care needs.
Some areas have limited availability; pricing can be higher than other options.
Varies depending on the plan and services.
A telehealth platform offering primary care, mental health services, and prescription refills.
Affordable pricing, convenient for routine care, and easy-to-use platform.
Limited availability in some areas, not suitable for urgent care needs.
Varies depending on the plan and services.

A telehealth platform offering virtual visits with doctors, therapists, and specialists.
Wide range of services, 24/7 availability, easy-to-use platform.
Pricing can be higher than other options; not all insurance plans are accepted.
Varies depending on the plan and services.
A HIPAA-compliant telehealth platform designed for healthcare providers.
Easy to use, free basic plan, integrates with electronic health records.
Limited features in the free plan, less robust than enterprise-level solutions.
Free, Basic, Professional, Enterprise.
A popular video conferencing tool widely used for telehealth consultations.
User-friendly, robust features, strong security measures.
Not specifically designed for healthcare, additional integrations may be needed.
Free, Pro, Business, Enterprise.
A collaboration and communication tool with telehealth capabilities.
Integrated with Microsoft 365, robust features, and a secure platform.
It can be complex for some users and may require additional setup.
Microsoft 365 plans.
A comprehensive video conferencing and collaboration platform.
Strong security, high-quality video and audio, and integration with other Cisco products.
It can be complex to set up; pricing can be high.
Varies depending on the plan and features.
A video conferencing tool integrated with Google Workspace.
Easy to use, free for personal use, and integrates with other Google products.
Limited features compared to other platforms, less robust security measures.
Free Google Workspace plans.
A comprehensive telehealth platform offering a wide range of services, including consultations with doctors, therapists, and specialists.
User-friendly interface, wide range of services, affordable pricing.
Limited availability in certain regions.
Varies depending on the services and region.
A telehealth platform focused on providing affordable healthcare for common conditions, including sexual health, mental health, and chronic disease management.
Affordable pricing, convenient, discreet.
Limited scope of services.
Varies depending on the service.
A leading telehealth company offering various virtual healthcare services, including medical consultations, mental health services, and chronic care management.
Wide range of services, 24/7 availability, easy to use.
Pricing can be higher than other options.
Varies depending on the plan and services.
A membership-based primary care practice that offers in-person and virtual care.
High-quality care and convenient access to healthcare providers.
Membership fees can be expensive, and limited land is available in certain areas.
Membership fees vary by region.
The rapid advancement of technology has ushered in a new era of healthcare delivery, telemedicine, and virtual healthcare. While these innovations offer numerous benefits, such as increased accessibility and convenience, they also present significant ethical considerations and challenges.
Safeguarding sensitive patient information is paramount. Robust cybersecurity measures must be implemented to prevent data breaches and unauthorized access.
Only essential patient data should be collected and stored, reducing the risk of exposure.
Patients should be informed about how their data will be collected, used, and shared and provide explicit consent for these practices.
Ensuring accurate diagnosis and effective treatment delivery remotely requires careful consideration of factors such as technology limitations, network connectivity, and potential delays in communication.
Healthcare providers must be adequately trained in telemedicine practices to maintain high standards of care.
Building a strong patient-provider relationship remotely can be challenging. Effective communication and empathy are crucial to establishing trust and rapport.
Clear and consistent reimbursement policies for telehealth services are essential to ensure financial sustainability for healthcare providers.
Reimbursement rates should reflect the value of telehealth services and the costs associated with providing care remotely.
Reimbursement policies should promote equitable access to telehealth services, particularly for underserved populations.
As you mentioned, 5G technology is poised to revolutionize telemedicine and virtual healthcare. With its high-speed, low-latency capabilities, 5G will enable:
Surgeons can perform complex procedures remotely with high-definition video and precise robotic control.
More seamless and interactive video consultations with reduced lag time.
Real-time vital signs and other health metrics monitoring, with faster data transmission and analysis.
AI is rapidly advancing, and its applications in healthcare are vast. We can anticipate:
AI can analyze patient data to predict disease outbreaks, identify high-risk individuals, and recommend preventive measures.
AI-powered drug discovery can accelerate the development of new treatments and therapies.
AI can analyze individual patient data to tailor treatment plans and optimize medication dosages.
IoMT devices are becoming increasingly sophisticated, enabling:
Wearable devices and implantable sensors can track vital signs, blood glucose levels, and other health metrics.
Real-time data from IoMT devices can be used to manage chronic conditions and prevent complications.
Early detection of diseases like diabetes, heart disease, and cancer through continuous monitoring and analysis of health data.
Blockchain can revolutionize healthcare by providing a secure, transparent, immutable patient data record. This can enhance:
Protecting patient data from breaches and unauthorized access.
We are facilitating the seamless exchange of health information between different healthcare providers.
Tracking the origin and authenticity of medical supplies and drugs.
Virtual and augmented reality can be used to:
Immersive simulations can provide hands-on training for medical students and healthcare professionals.
Virtual reality can be used to educate patients about their conditions, treatment options, and self-care strategies.
Virtual reality can distract patients during medical procedures, reducing pain and anxiety.
Telemedicine and virtual healthcare, powered by AI, are transforming the healthcare landscape. By offering convenience, accessibility, and improved outcomes, these innovative approaches have the potential to revolutionize how we deliver and receive healthcare. However, addressing ethical considerations and challenges is essential to ensure that the benefits of these technologies are maximized while minimizing potential risks. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more exciting developments in the field of telemedicine and virtual healthcare.
